Acne Rosacea – Exploring Causes and Treatments | AcneSkinGuide
Summary of Acne Rosacea
Rosacea is a prevalent but frequently misunderstood chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, and pimples. It has four main subtypes involving different combinations of these symptoms. While the exact causes are unknown, factors like genetics, environmental triggers, demodex mites, and hormones are believed to play a role. Though incurable, rosacea can be managed through oral/topical medications, laser treatments, lifestyle changes, and gentle skincare.
However, it poses challenges like unpredictable flare-ups, treatment side effects, and a significant emotional toll on self-esteem. Despite the difficulties, early diagnosis, consistent treatment, avoiding personal triggers, and building a support system can help minimize rosacea’s impact. Ongoing research aims to improve therapies and understanding of this complex condition affecting millions worldwide.

Acne Rosacea: The Misunderstood Skin Condition
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects an estimated 16 million Americans. Despite its prevalence, rosacea is widely misunderstood and often goes undiagnosed or undertreated. This article aims to shed light on this complex condition, its causes, symptoms, treatments, and the challenges faced by those living with it.
Understanding Rosacea
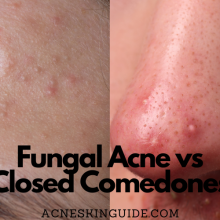
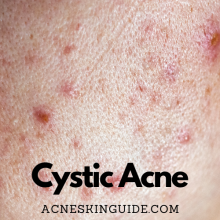
Rosacea is characterized by persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, and pimples that often resemble acne. It primarily affects the central areas of the face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. Contrary to popular belief, rosacea is not caused by poor hygiene or diet alone.
There are four main subtypes of rosacea: erythematotelangiectatic (redness and flushing), papulopustular (bumps and pimples), phymatous (thickened skin, often on the nose), and ocular (eye irritation and redness). Many individuals experience a combination of these symptoms, and the condition can progress through various stages, ranging from occasional flushing to more severe, persistent inflammation and skin changes.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but researchers believe it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with fair skin, particularly those with Celtic or Scandinavian ancestry, are at a higher risk of developing rosacea.
Environmental triggers, such as sun exposure, stress, alcohol consumption, spicy foods, and certain skincare products, can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Additionally, demodex mites, microscopic organisms found on everyone’s skin, may overpopulate in rosacea patients, contributing to inflammation.
Hormonal factors, like menopause in women and androgen imbalances in men, can also play a role in the development and progression of rosacea.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for rosacea, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Oral and topical medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, are often prescribed to reduce redness, bumps, and pimples.
Laser and light therapies, like intense pulsed light (IPL) and pulsed dye lasers, can effectively remove visible blood vessels and calm inflammation. Procedural treatments, like laser resurfacing, dermabrasion, and chemical peels, can also provide longer remission periods.
Combination therapy, which involves using medications and procedures together, is often considered the most effective long-term approach for managing rosacea.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle and dietary changes can significantly impact symptom management. Identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as stress, alcohol, and certain foods, is crucial. Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and mineral-based makeup can also help soothe sensitive skin.
For those with ocular rosacea, specific treatments like eye drops, warm compresses, and avoiding triggers that irritate the eyes are essential.
Living with Rosacea
Rosacea can have a profound emotional impact on those affected, leading to embarrassment, anxiety, and depression. The visible symptoms can take a toll on self-esteem and confidence, especially in social or professional settings.
Building a support network, joining online communities, and seeking professional counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with rosacea. Additionally, learning makeup techniques to neutralize redness and cover up bumps can boost confidence.
Accommodations in the workplace, such as informal dress codes and temperature control, may be necessary for some individuals to manage their symptoms comfortably.
Downsides and Challenges
Despite the available treatments, managing rosacea can be a lifelong battle for many individuals. Flare-ups can be unpredictable and frustrating, even with diligent trigger avoidance and medication adherence.
Some treatments, like oral antibiotics, can have side effects or become less effective over time, necessitating adjustments or alternative approaches. Laser and procedural treatments can be costly and may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
Additionally, the psychological impact of rosacea should not be underestimated. The constant vigilance required to manage triggers and the potential for embarrassing flare-ups can take a significant toll on mental health and overall quality of life.
While ongoing research aims to uncover more effective therapies and potential cures, rosacea remains a challenging condition to manage for many individuals.
The Road Ahead
Rosacea is a complex and often misunderstood skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is no cure yet, early diagnosis and consistent treatment can help individuals gain better control over their symptoms and minimize the impact on their daily lives.
Increased awareness and education about rosacea are crucial to destigmatizing the condition and encouraging those affected to seek proper medical care and support. By fostering a supportive community and prioritizing research efforts, the road ahead holds promise for improved treatments and a better understanding of this multifaceted condition.
FAQs and Answers
Is rosacea contagious or caused by poor hygiene?
No, rosacea is not contagious or caused by poor hygiene. Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with causes that are not related to hygiene practices or spread through contact with others.
The main factors that contribute to the development of rosacea include:
Genetics – There seems to be a hereditary component, as rosacea tends to run in families. Those with fair skin and European/Celtic ancestry are at higher risk.
Environmental triggers – Sun exposure, stress, alcohol, spicy foods, extreme temperatures, and certain skincare products can aggravate and worsen rosacea symptoms.
Demodex mites – An overpopulation of these microscopic mites that live on everyone’s skin may play a role in inflammation for some rosacea sufferers.
Immune system dysregulation – An overactive inflammatory response and dysfunction of proteins in the immune system is thought to be involved.
No, rosacea is not contagious or caused by poor hygiene. Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with causes that are not related to hygiene practices or spread through contact with others.
The main factors that contribute to the development of rosacea include:
Genetics – There seems to be a hereditary component, as rosacea tends to run in families. Those with fair skin and European/Celtic ancestry are at higher risk.
Environmental triggers – Sun exposure, stress, alcohol, spicy foods, extreme temperatures, and certain skincare products can aggravate and worsen rosacea symptoms.
Demodex mites – An overpopulation of these microscopic mites that live on everyone’s skin may play a role in inflammation for some rosacea sufferers.
Immune system dysregulation – An overactive inflammatory response and dysfunction of proteins in the immune system is thought to be involved.
While hygiene habits like gentle, non-irritating cleansing can help manage rosacea, poor cleanliness does not actually cause or spread the condition itself. It arises from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and inflammatory factors, not due to lack of hygiene or any infectious process.
Can certain makeup and skincare products worsen rosacea?
Yes, lifestyle factors can potentially override or mitigate the effects of a genetic predisposition to acne to some extent.
While genetics play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to acne, lifestyle factors and environmental exposures can influence the expression and severity of the condition. Here’s how lifestyle factors can impact acne development:
- Diet: Certain dietary patterns, such as a diet high in refined carbohydrates, dairy products, and unhealthy fats, have been associated with an increased risk of acne. Adopting a balanced, nutrient-rich diet can help regulate hormonal levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall skin health.
- Stress management: High levels of stress can trigger hormonal imbalances and inflammation, both of which can exacerbate acne. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or exercise can help manage stress levels and potentially reduce the severity of acne.
- Sleep patterns: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, including skin health. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormone levels and increase inflammation, contributing to acne flare-ups.
- Skincare routine: Proper skincare practices, such as gentle cleansing, avoiding excessive irritation, and using non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products, can help prevent acne breakouts or minimize their severity.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers like certain medications, cosmetic products, or environmental exposures that may worsen acne can help manage the condition.
It’s important to note that while lifestyle modifications can be beneficial, they may not completely override a strong genetic predisposition to acne. However, they can certainly help reduce the severity and frequency of breakouts, even in individuals with a genetic predisposition.
Yes, certain makeup and skincare products can definitely worsen or trigger flare-ups of rosacea symptoms. The skin of those with rosacea is very sensitive and easily irritated, so it’s important to use gentle, non-irritating products.
Some ingredients that are commonly problematic for rosacea include:
Alcohol – Found in many toners, astringents, and some makeup removers. Can cause stinging, flushing, and dryness.
Fragrance – Synthetic fragrances are a major irritant that can induce redness, bumps, and burning sensations.
Menthol/Mint – Gives a cooling sensation but also triggers flushing reactions in many.
Witch hazel – An astringent that strips the skin and causes dryness/irritation.
Sodium lauryl sulfates – Foaming agents found in many cleansers that can be drying and inflammatory.
Retinoids – While beneficial for some, retinol products may be too harsh for rosacea-prone skin.
In addition, abrasive scrubs, rough washcloths, and over-exfoliating can worsen rosacea by damaging the skin’s protective barrier.
It’s best for those with rosacea to use fragrance-free, non-comedogenic, and “rosacea-friendly” labeled products without harsh ingredients. Mineral makeup is also preferable over oil-based or irritating formulas. Being mindful of product ingredients is key to avoiding unnecessary flare-ups.
What is the relationship between rosacea and the gut/digestive system?
There does appear to be an important link between rosacea and gut/digestive health. While the exact mechanisms are still being researched, here are some of the key connections:
Inflammation
Rosacea is an inflammatory condition, and chronic inflammation in the gut may contribute to overall elevated inflammation levels that manifest in rosacea flare-ups. Gut disorders like inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and leaky gut syndrome are associated with higher rosacea risk.
Microbiome Dysbiosis
An imbalance in the gut microbiome (bacteria, fungi, etc.) may play a role. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) seems more prevalent in rosacea patients. Restoring healthy gut flora may help.
Food Intolerances
Many rosacea sufferers find their symptoms are triggered by certain foods like spicy items, alcohol, dairy, or histamine-rich foods. This points to a digestive component in rosacea flares for some individuals.
Gut Permeability
A “leaky gut” where partially digested food particles and bacteria enter the bloodstream can increase systemic inflammation that shows up as rosacea symptoms.
Small Intestine Bacteria
H.pylori bacteria overgrowth has been linked to higher incidences of rosacea as well.
While the gut-skin connection is still being clarified, improving gut health through dietary changes, probiotics, and treating underlying GI issues may provide benefits for rosacea patients by reducing whole-body inflammation.
Are there any new or emerging treatments for rosacea on the horizon?
Yes, there are several promising new and emerging treatments for rosacea currently in development or undergoing clinical trials:
- Topical Mirvaso (brimonidine)
This topical gel is already FDA-approved for treating persistent facial erythema (redness) of rosacea. However, a longer-acting formulation is in development that could provide redness relief for 12+ hours. - Anti-inflammatory Cream (PRX-106)
This investigational topical cream contains two anti-inflammatory compounds that inhibit overactive inflammatory pathways involved in rosacea. Phase 3 trials are assessing its ability to treat papules and pustules. - Xyway (minocycline) Foam
An antibiotic foam formulation of minocycline is being studied as a new way to deliver the medication directly into the skin’s hair follicles where rosacea inflammation begins. - RVX-208
This oral medication works by inhibiting inflammatory proteins in a novel way. It has shown promise in early trials for reducing lesions and redness. - Light Therapy Devices
New at-home LED light therapy devices that emit specific wavelengths are being developed as a gentle anti-inflammatory option for rosacea. - Neurotoxins (Botox, etc.)
Injections of neuromodulators like Botox are being explored to temporarily reduce flushing and redness by blocking nerves that trigger facial flushing.
While more research is still needed, these emerging options could provide new pathways for treating the various aspects of rosacea more effectively in the future.
How can rosacea be effectively treated or managed during pregnancy?
Managing rosacea during pregnancy requires some special considerations, as certain treatments may not be recommended. Here are some tips for effectively treating and managing rosacea while pregnant:
Medications
Many oral antibiotics used for rosacea like tetracyclines are not advised during pregnancy. Topical metronidazole gel is considered safe. Always consult your dermatologist before using any medications.
Laser/Light Therapies
Procedures involving lasers, intense pulsed light (IPL), or photodynamic therapy should be avoided during pregnancy as a precaution.
Identify Triggers
Hormonal changes can worsen rosacea flares, so keeping a diary to pinpoint personal triggers like specific foods, products, or activities is very helpful during this stage.
Gentle Skincare
Use an ultra-gentle, fragrance-free skincare routine formulated for sensitive skin. Look for products labeled “non-comedogenic” and “hypoallergenic.”
Mineral Makeup
Mineral powder-based makeup can help neutralize redness while avoiding irritation from other makeup ingredients.
Cool Compresses
Applying cool compresses or rinsing with cool water can provide relief from facial flushing and burning sensations.
Sun Protection
Wear protective clothing and use a physical sunscreen with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide daily to prevent sun-triggered flares.
Relax and De-Stress
Find ways to de-stress through prenatal yoga, meditation, or other calming activities, as stress can aggravate rosacea.
While oral prescriptions may be limited, a gentle routine focused on avoiding triggers, gentle skin care, and lifestyle remedies can help manage rosacea effectively during pregnancy. Communicating with your dermatologist is key.